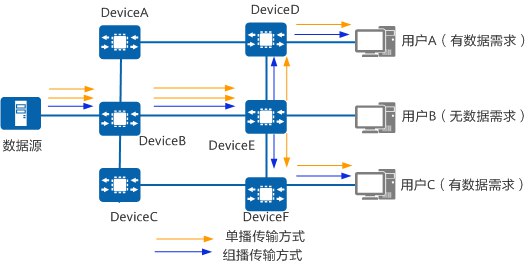
Unicast: Sending data to a single destination host, where each unicast packet has a unicast IP address as its destination address
- Transmission Method: Point-to-point transmission
- Drawback: Requires establishing separate data channels between the sender and each receiver
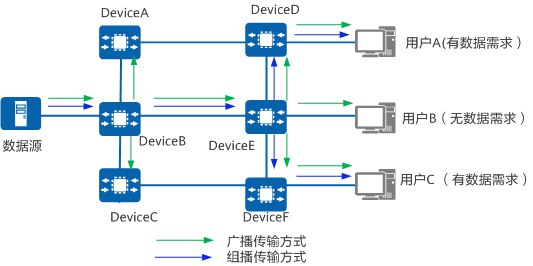
Broadcast: Sending data to all hosts within the same broadcast domain or subnet
- Transmission Method: Point-to-multipoint transmission
- Drawback: Sends unnecessary data to irrelevant hosts within the subnet
Multicast: When certain users in the network need specific data, the sender only needs to send multicast data once. Through multicast protocols, a multicast distribution tree is established for multicast packets. The data begins to replicate and distribute once it reaches the router closest to the users
- Transmission Method: Point-to-multipoint transmission
- Advantages:
- Improves data transmission efficiency
- Reduces the possibility of backbone network congestion
- Compared to unicast, multicast ensures that identical packets appear at most once on each link
- Compared to broadcast, multicast packets are sent on-demand and can be transmitted across network segments